How To Become An Obstetrics Nurse?
Learn how to become an obstetric nurse. This informative guide provides valuable insights and steps to help you pursue a rewarding career in obstetrics. Discover the education, skills, and training needed to excel in this specialized nursing field. Start your journey toward becoming an obstetric nurse today.
What is an obstetric nurse?
Nurses specializing in obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) care for pregnant women and their newborns throughout their whole reproductive life cycle. Their mission is to ensure the health of women and their unborn children by close monitoring throughout pregnancy. When emergencies arise, obstetric nurses also step in to help.
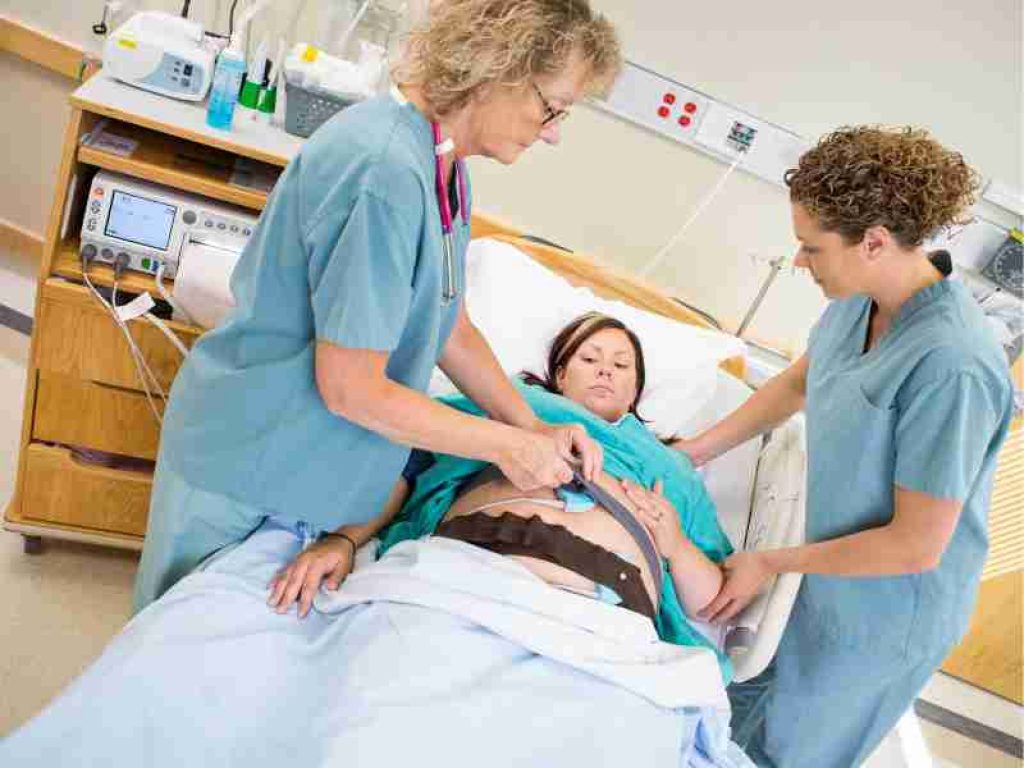
Most of the public believes that an obstetrician’s only responsibility is to assist in delivering babies. Yet there is so much more to this position than that! Nurses specializing in obstetrics work with doctors to support expectant mothers throughout pregnancy, from preconception care to delivery and beyond. OB nurses create a personal connection with pregnant women, from their first meeting to childbirth and beyond.
What are the duties of an obstetrician-gynecologist nurse?
The duties of an obstetric nurse include:
- Assisting with prenatal care, including physical exams and ultrasounds
- Educating patients on nutrition, exercise, and other lifestyle changes to ensure a healthy pregnancy
- Monitoring fetal development and providing support during labor and delivery
- Administering medications and treatments as prescribed by the physician
- Assisting with postpartum care, such as breastfeeding
While tasks for an OB nurse can vary depending on the company they work for, the atmosphere in which they do their work is a major factor. Common subspecialties within obstetric nursing include:
Obstetrics Nursing
Pregnancy, labor, delivery, and postpartum care are all part of obstetrics. Nurses specializing in maternal and fetal health care provide a wide range of services to pregnant mothers. Specifically, your duties will consist of the following:
- Guiding expecting mothers through making informed decisions about family planning, fertility, and their health.
- Checking the mother-to-vital signs, Babe’s urine and blood samples, and performing ultrasounds on the fetus.
- Informing clients of potential dangers and available remedies in the event of abnormal pregnancies or other issues.
- Preparing the patient and the birth control room.
- Delivering babies and helping obstetricians and midwives.
- Supporting laboring mothers with pain relief, care, and continuous fetal monitoring.
- Taking a baby’s temperature, pulse, and respiration rate, as well as completing other standard checks following delivery.
- Teaching new parents the fundamentals of caring for their care, such as breastfeeding, diapering, swaddling, feeding, bathing, and nutrition.
- Postpartum health checks for mothers.
- Taking care of babies by bathing, measuring, weighing, and vaccinating them.
Gynecological Nurse
Regarding women’s health, gynecologists are primarily concerned with issues of physical and sexual health, such as the prevention and treatment of disease. Tasks unique to this division include:
- Patient education and counseling on STI avoidance, contraception, fertility options, and safe sexual behavior.
- Regular gynecological checkups and additional diagnostics as needed.
- Conducting fundamental breast checks in search of cancer and informing patients on the importance of mammography screenings.
- Gathering thorough medical histories to guide treatment planning.
- Helping people with Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and other reproductive health problems.
Obstetrics Nurse Responsibilities
- Inform pregnant ladies, leading them through each trimester and fielding their questions.
- Assist patients in getting ready for their doctor visits by performing routine checks and keeping detailed records.
- Keep an eye on the pregnant woman and report any changes to her doctor.
- During the stressful and emotional phase of pregnancy, you can help patients by reducing their anxiety by paying attention to their mental health.
- Provide medical assistance during labor, delivery, and any necessary surgical procedures.
How to Become an Obstetrics Nurse?
The path to becoming an obstetrics nurse involves several major milestones. They must first earn a nursing degree, either an associate’s or a bachelor’s. They then need to get their RN license. After that, they are qualified to enter the nursing profession. Clinical expertise as an OB/GYN nurse is required before one may apply for certification in this field.
Obtain a Nursing Degree (RN, ADN, or BSN)
A nursing degree is required for anyone looking to enter the nursing profession. This is because obtaining a nursing license involves formal education. The Associate of Science in Nursing (ASN) can be earned in two years, whereas the Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) takes four years to complete (BSN).
During the 2020-21 academic year, the average cost of a four-year public university education was $9,400, while the cost of a two-year public university education was $3,900. These figures come from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES). With their increased skill set, BSN nurses find work easier. Numerous ADN-holding nurses continue their education in the field to get BSNs.
Get a license as a registered nurse.
One must become licensed as a registered nurse (RN) after completing their nursing education. To become a registered nurse (RN), one must take and pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN). The registration fee for this test is $200.
Although the NCLEX-RN is a prerequisite in every state, other steps must be taken to get a license as a registered nurse. The Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC) is a group of states that mutually accept each other’s nursing licenses, making it possible for nurses to practice in any member state.
Find a Job in an Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinic
After earning their nursing credentials, nurses should seek employment at an obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) clinic. They’ll get hands-on experience assisting pregnant women and new mothers in this setting. Payscale reports that as of 2021, an obstetrics nurse with less than a year of experience might expect to earn a median annual pay of $50,460.
Apply for Accreditation
Obtaining certification as an inpatient obstetric nurse is possible through the National Certification Corporation’s specialized gynecological certification computer-based exam. Registration for the exam is $325.
In order for applicants to become certified, they must have worked at least two years of inpatient maternity care as a registered nurse and accumulated 2,000 hours of clinical experience. The application and examination process is open year-round; however, candidates must complete the examination within 90 days of being notified of their eligibility.
What is the typical wage for an obstetrician-gynecologist nurse?
An OB nurse can earn a median annual salary of $107,736. The wage of an obstetrical nurse may change depending on the nurse’s level of training, the hospital where she works, and the number of years she has been employed there.
Pay for nurse practitioners and other forms of advanced practice nursing is typically much greater than that of less experienced nurses. Private practice obstetricians earn more money than their hospital-based counterparts or non-profit-sector counterparts.
What is the job description of an Obstetrics Nurse?
An obstetric nurse supports expectant mothers throughout their pregnancies and beyond the delivery process. An obstetrics role can expand over time to include the management of teams or the care of pregnant patients experiencing complications.
Those who have earned a Master’s degree in Nursing may attain certification as a Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM) upon completion. These nurse practitioners can legally act independently and frequently serve as obstetrics nurses’ supervisors.
FAQ’s
What does OB stand for in medical terms?
A medical specialty concerned with the care, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions affecting the female reproductive system, including pregnancy, delivery, and menstruation.
What is an obstetric nurse?
An obstetric nurse is a specialized healthcare professional who provides care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum. They work closely with pregnant women, assisting in prenatal care, monitoring fetal development, and supporting the delivery process.
What qualifications do I need to become an obstetric nurse?
To become an obstetric nurse, you must complete a nursing education program, such as a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) or an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN). After completing your nursing program, you must pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN) to become a licensed nurse.
Are there any specific certifications required to become an obstetric nurse?
While certification is not mandatory, obtaining specialized certifications in obstetric nursing can enhance your career prospects and demonstrate your expertise in the field. The National Certification Corporation offers Inpatient Obstetric Nursing (RNC-OB) and Electronic Fetal Monitoring (C-EFM) certifications that can help showcase your knowledge and skills.
What skills are essential for an obstetric nurse?
Obstetric nurses require a range of skills to provide comprehensive care to pregnant women. Some essential skills include strong communication and interpersonal abilities, critical thinking and problem-solving skills, knowledge of prenatal and postpartum care, and the ability to handle stressful situations with compassion and empathy.
How can I gain experience as an obstetric nurse?
Gaining experience as an obstetric nurse can be achieved through various avenues. Consider seeking employment in labor and delivery units, postpartum units, or antepartum units within hospitals or birthing centers. Additionally, volunteering or completing clinical rotations in obstetrics during your nursing education can also provide valuable experience.
What are the typical duties of an obstetric nurse?
Obstetric nurses have diverse responsibilities, including conducting prenatal assessments, monitoring fetal heart rates, providing education and support to expectant mothers, assisting during labor and delivery, administering medications, and ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the baby.