What Is An Obstetric Nurse?
Discover the vital role of an obstetric nurse in providing compassionate care throughout pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum. Gain insights into their responsibilities, specialized training, and their impact on the health and well-being of expectant mothers and newborns. Explore the world of obstetric nursing in this informative guide.
What Is an Obstetric Nurse?
An obstetric nurse is a registered nurse who has completed further training in caring for women throughout pregnancy, labor, and after giving birth. Nurses caring for pregnant women and newborns are referred to as perinatal nurses. An obstetric nurse’s duties include taking vital signs, giving out drugs, helping deliver, and comforting the patient and their family.
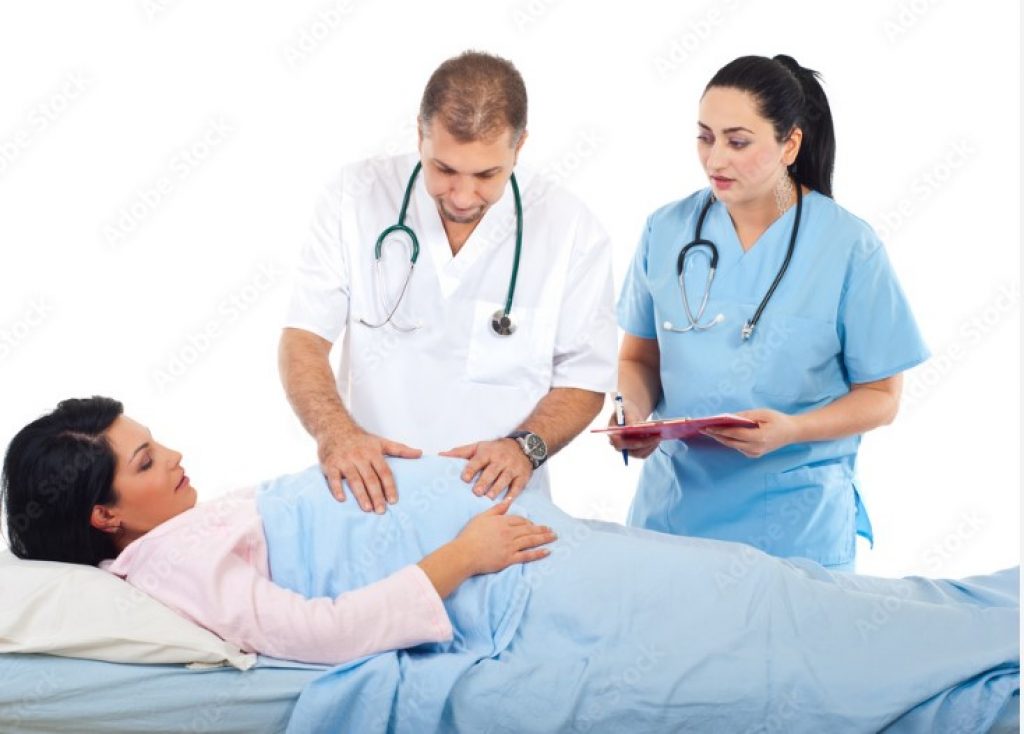
These devoted nurses collaborate with obstetricians, midwives, and other medical staff to make childbirth as healthy and comfortable as possible for both mother and child. Becoming an obstetric nurse could be a satisfying career path for those interested in nursing and women’s health.
A woman’s best resource before, during, and after her nine-month pregnancy is a trained obstetric specialist. Despite the centrality of obstetricians at this stage in a woman’s life, the contribution of obstetric nurses should be recognized. These nurses are experts in caring for expectant mothers and their newborns before, during, and after childbirth. An obstetric nurse may offer support and counseling when a woman tries to conceive.
What does an Obstetric Nurse do?
Pregnant women can rely on the expertise of OB nurses. They must be aware of the breadth and depth of issues that can arise for pregnant women. A pregnant woman living with HIV may need additional care or monitoring in the early stages of her pregnancy. Women with major medical conditions are usually monitored more frequently than those without health issues, including those with conditions such as a weakened heart, diabetes, cancer, or other ailments.
Pregnant women who use certain medications or have certain physical or mental impairments may require further evaluation, monitoring, or treatment to ensure the health and safety of themselves and their unborn children.
Many potential problems can occur during pregnancy. Several pregnancy-related issues can harm the mother’s health, including gestational diabetes, fetal complications, significant morning sickness, nausea, and exhaustion.
Other complications often arise in the third trimester of late pregnancy. Some pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia, toxemia, placenta previa, and premature delivery, can be fatal for both the mother and the child.
An obstetrics nurse must be trained to care for patients with these diagnoses. The nurse’s ability to maintain composure and provide soothing words to a pregnant patient under stress is crucial. In addition, effective and timely communication between the nurse, doctor, and other healthcare providers is essential in this position.
What are the Skills of Obstetric Nurses?
Obstetric nurses possess a wide range of skills crucial in providing quality care throughout pregnancy, labor, and postpartum. Here are the key skills of an obstetric nurse:
Assessment and monitoring:
Obstetric nurses are adept at assessing pregnant women’s and unborn babies’ health status. They monitor vital signs, fetal heart rate, and any signs of complications.
Labor support:
These nurses provide emotional and physical support to women in labor, helping them manage pain, facilitating comfort measures, and assisting with breathing techniques.
Neonatal care:
Obstetric nurses are trained in newborn care, including performing initial assessments, administering medications, and facilitating breastfeeding.
Patient education:
They play a vital role in educating expectant mothers and their families about prenatal care, childbirth, postpartum recovery, and infant care.
Emergency response:
Obstetric nurses are prepared to handle emergencies during childbirth, such as bleeding, fetal distress, or emergency cesarean sections. They are trained in resuscitation techniques for both mother and baby.
Communication and teamwork:
Effective communication and collaboration with the healthcare team, including doctors, midwives, and other nurses, are paramount in providing holistic care to the mother and baby.
Cultural competence:
Obstetric nurses respect and embrace the diversity of their patients, recognizing the importance of cultural values and beliefs in providing individualized care.
Where Does An Obstetric Nurse Work?
OB nurses can find employment in the following workplace settings:
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (OB/GYN) physician’s office
- Hospital Maternity Ward
- Midwife Practice
- Family Planning Center
- Private Birthing Centers
- Urgent Care Clinics
- Community Clinics
How to Become an Obstetric Nurse?
There are various crucial measures to take to enter the field of obstetric nursing. To become an obstetric nurse, one must earn a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree from an accredited nursing college. To acquire the requisite obstetrics-specific skills and knowledge, it is also crucial to have clinical experience in a labor and delivery setting.
To further improve employment opportunities and show dedication to professional growth, obtaining RN certification is essential. Expertise in obstetrics can be bolstered through participation in continuing education programs and the completion of specialized training programs.
The final step to becoming a top-notch obstetric nurse is to secure a position in a labor and delivery unit or obstetrics department, where you may gain practical experience and hone your abilities. A successful career in obstetric nursing awaits those who take the time to follow these guidelines.
What qualifications are required to become an obstetrics nurse?
You require formal training as a nurse to work in obstetrics. An ADN or BSN of four years will suffice for this purpose. Following that, it is necessary to successfully complete the NCLEX exam in order to obtain registration as a nurse in your state. You can work as an obstetrics nurse once you’ve completed the necessary training.
You can pursue more training and certification once you’ve started working as an obstetrics nurse. You can sit for certification exams to demonstrate your competence as an obstetrics nurse. After completing an advanced degree program in nursing, it is possible to become a nurse midwife and work independently.
What is the difference between an Obstetric Nurse and a Midwife?
There are some key variations between the responsibilities of midwives and obstetric nurses. Registered nurses with additional training in obstetrics work under the supervision of physicians to provide prenatal care and delivery assistance to expectant mothers.
However, midwives are doctors who specialize in caring for women throughout their lives, not just during pregnancy. They may prioritize natural and low-intervention deliveries and take a more comprehensive view of the process.
How much does an Obstetric Nurse make?
The BLS reports that the median annual wage for registered nurses, which includes OB nurses, is $81,220. Various variables, including but not limited to your level of education, years of experience, credentials, and the industry you work in, will determine your exact compensation. Compare average nursing salaries across the country.
What is the Career Outlook for Obstetric Nurses?
Through 2031, the BLS projects an overall 6.2% increase in demand for RNs. There will be a demand for many of these 195,400 new RN positions in obstetric nursing and related disciplines serving women. There is a need for fresh OB nurses since, like in other nursing fields, many experienced nurses are reaching retirement age.
FAQ’s
What is an obstetric nurse?
An obstetric nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in providing care to women during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum. They are trained to support the mother and the newborn, ensuring their safety and well-being.
What is the role of an obstetric nurse during labor and delivery?
An obstetric nurse plays a crucial role in providing care and support to the mother during labor and delivery. They monitor the progress of labor, assess vital signs, administer medications as needed, and provide emotional support and encouragement. They also assist the physician or midwife during procedures, such as episiotomies or cesarean sections, and ensure a safe and positive birthing experience for both the mother and the baby.
Can obstetric nurses work in other healthcare settings?
Yes, obstetric nurses can work in various healthcare settings apart from hospitals. They may also work in birthing centers, clinics, maternity wards, or patients’ homes as part of home healthcare services. The role of an obstetric nurse may vary depending on the setting, but their main focus remains on providing care and support to expectant mothers and their babies.
How important is the role of an Obstetric Nurse?
The role of an Obstetric Nurse is extremely important as they play a vital role in ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and baby during the pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum periods. They provide essential medical care, emotional support, and education to women and their families, helping them navigate the journey of pregnancy and childbirth safely.